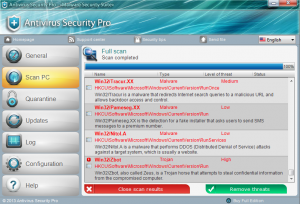
The Following Article is a evaluation report by Chinese e-government
network on United State network security management with interesting
conclusion at end.published today on e-gov.org.cn.
As early as 2009, U.S. President Obama announced that cyberspace has
become a threat to the economic and national security threat of the
21st century, the United States faced the most serious. May 2009, he
directed the U.S. Government Accountability Office (US Government
Accountability Office, GAO) review of U.S. national cybersecurity
policies and procedures. Examination report showed the presence of two
important deficiencies: the lack of clear distinction between the task
and the lack of strong leadership among federal agencies. Although the
White House three years ago, the addition of a new Special Assistant to
the President and the "Network security coordinator" responsible for
network collaboration among federal agencies leading the coordination
and synchronization, the U.S. Government Accountability Office concluded
given the overall evaluation is : U.S. National Security management
needs to make greater improvements. The main purpose of this paper is
threefold: (1) determine the different agencies within the U.S.
government network security management tasks, duties and powers; (2)
assess the efficiency and effectiveness of the United States national
cybersecurity management plan; (3) proposed to enhance the overall
network security management strategy proposal is that in order to
effectively protect and operations in the United States of network and
information resource-constrained environment.
"Network security threats is one of the most serious problems in
national security, public safety and economic challenges facing our
country as a whole and so."
- 2010 U.S. "National Security Strategy"
Today's hackers are no longer thrill-seeking teenagers, they are
organized crime groups, the national armed forces and non-state actors,
they spying on people and infrastructure or malicious conduct, to the
detriment of U.S. national security and / or economic interests.
Although thousands of miles away, but the technology has become more
sophisticated foreign hackers can penetrate U.S. computer networks to
steal sensitive electronic military technology. In 2009, U.S. President
Barack Obama gave to all American citizens nationally televised speech
said, "Every day we see thousands batch Network thieves repeatedly steal
(our) sensitive information - they are those domestic disgruntled
employees, Trinidad Hackers individual, industrial espionage and,
increasingly, foreign intelligence services outside the "speech of
President Obama's intention is to warn U.S. citizens: a key U.S.
security interests are attacked, in order to protect the American
people, their assets, and the United States national interest, a timely
and effective U.S. network security strategy action plan must be
implemented as soon as possible. President Obama went on to explain that
"this is a great irony of our Information Age - Those who help us to
manufacture and develop the technology, but also to help those who
disrupt and destroy our enemies" as countries transition from the
industrial age to the information age, President warned the majority of
the American people, those new technologies to promote progress in the
world is also counterproductive, effective measures must be taken to
reverse this trend.
In order to change the use of advanced technologies for computer
hackers luck cybercrime, must develop a new and groundbreaking strategic
plan of action to change the current network failure mode. Develop such
a plan must include the U.S. government, the international community
and the private - the active participation of the public sector, through
an independent authority on U.S. cybersecurity stakeholders leadership,
guidance and encouragement. The purpose of this paper is to assess the
current environment and significant authority to a better understanding
of network security management structure, and then how to carry out a
reasonable plan of action, and get a good national network security
situation made program recommendations in the future. The main purpose
of this paper is threefold: (1) determine the different agencies within
the U.S. government network security management tasks, duties and
powers; (2) assess the efficiency and effectiveness of the national
network security management plan; (3) proposed overall strategic plan to
improve network security management recommendations to the limited
resources and effective protection of the environment in the United
States of network operations and information.
Background
In 2008, in response to the continuing threat of cyber attacks on
federal systems and services brought about by President George W. Bush
authorized the implementation of a new "comprehensive national
cybersecurity plan (Comprehensive National Cybersecurity Initiative,
CNCI)". The program aims to improve the capacity of the federal
government to protect sensitive information, to prevent hackers invade
the country and the nation-state institutions network and other
networks. In addition, because a number of departments reported that
they suffer from a number of computer networks from cyber attacks, the
U.S. government decided to implement a "comprehensive national
cybersecurity plan." Also established the National Cyber Security
Center (National Cyber Security Center, NCSC) to coordinate
information on the various federal agencies and departments to ensure
network security and facilitate collaboration. "National Cyber
Security comprehensive plan" aimed at reducing vulnerabilities,
intrusion prevention, and predict potential threats, and the National
Cyber Security Center is committed to standardize the current network
security processes, and the introduction of new policies and business
practices to better protect the computer networks and systems.
As early as 2009, U.S. President Barack Obama had announced that
"cyberspace has become a threat to the economic and national security
threat of the 21st century, the United States faced the most serious"
and that "the United States in the economic prosperity in the 21st
century will depend on cybersecurity." . May 2009, he directed the U.S.
Government Accountability Office to review the U.S. national
cybersecurity policies and procedures. Review the results of the policy
of the U.S. Government Accountability Office focused on network security
above responsibilities. David • Bowral authored Government
Accountability Office report, and noted the presence of two major
shortcomings: (1) lack of strong leadership. The lack of a clear
distinction between tasks (2) federal agencies. Concern about the lack
of strong leadership began in March 2009, when he was director of the
National Cyber Security Center • Rod Beckstrom suddenly to the U.S.
Department of Homeland Security (Department of Homeland Security, DHS)
Director submitted a letter of resignation claiming that the lack of
financial support and not the network security as a national priority
development projects, resulting in his decision to resign. Given Mr.
Beckstrom's sudden departure for the United States Government
Accountability Office and the National Cyber Security posture
assessment findings, U.S. President Barack Obama decided to establish a
special assistant to the president and "network security coordinator" in
the White House, aimed at improving inter-agency Collaboration with
synchronized efficiency. "Network security coordinator" This new
position will be responsible to the National Security Council (National
Security Staff, NSC) and the National Economic Council (Staff of the
National Economic Council) report, taking on network security management
services throughout the United States, the long-term development of
network security planning. To lead a national network program, President
Obama in December 2009 appointed Howard Schmidt as the country • A •
"Network security coordinator," Howard • A • Schmidt worked for the FBI,
specializing in cyber crime, has Microsoft and eBay served as the
company's chief security officer, also served as George W. Bush's White
House cybersecurity adviser. "Network security coordinator" neither
command, there is no budget authority for any federal agency, in today's
information age, to solve those problems in the U.S. and the world a
lot of network security issues, the size of his administrative staff is
not enough The.
Since December 2009, all federal agencies in the network business
and policy developments have made significant progress, but the lack of a
collective mechanism and collaboration between the various agencies
have been left behind until now. Although the "Network security
coordinator" has been appointed in government departments, needs an
urgent need to strengthen the leadership and management in monitoring
national cybersecurity programs have only recently been put on the
agenda. During the Government Accountability Office to conduct periodic
review of network security management, policies and programs when
determining who is the owner of the network security leadership and
decision-making duties, the division of responsibilities between federal
agencies have complained about the confusion, because the tasks and
responsibilities of the distinction is not clear, repeat duplication of
efforts and resources among agencies still exist, which resulted in
unnecessary confusion and waste. Some people think that repetitive work
and duplication of resources will enhance the country to some extent,
and / or increase productivity and network security posture, because
redundant network security personnel and equipment conducive to better
fulfill its mandate. However, due to lack of policy, leadership,
administration and information sharing, network security management is
difficult to obtain greater progress. Since the start of each federal
agency to develop a similar policy; monitor and maintain the same
network; investigating criminal acts; coordination with international
and domestic private and public sectors; and perform similar research
and development responsibilities for ordinary observer ( U.S. citizens),
this repetitive work is clearly a waste of the federal government,
state government and industry funding, and national security threats has
continued to rise. As the history books tell the story of the West,
Wild West is defeated and tamed, the victory by the right leadership,
reasonable structure and disciplined organization and a clear strategy
and a clear vision achieved, rather than through loose committees,
groups and by consensus vague blurred vision to guide policies, programs
and made a list. Therefore, the federal government needs to develop and
implement new network security strategy, this new network security
strategy requires summarize lessons of the past and expected future
demand. If only the development of the kind of "passive strategy" and
implement "hasty patchwork" solution, it would only make the country in a
passive network security dilemma. The world that the United States is
the world's technology leader in the development and leadership. As
cyber threats continue to spread rapidly around the world, and caused
great damage to the economic and security interests, the world needs a
role model for the network to achieve effective change, and positive
achievements. America needs to lead and to have this ability!
Tasks and responsibilities
Since the 1980s, network security has always been a thorny problem
of the U.S. government, but to tame the wild west was once also a thorny
issue. To better understand the network "mesh" Managing complexity in
the status quo, which clearly within the core sectors of the U.S.
government to develop national cybersecurity policies and operating
procedures bears responsibility is very important. In 2010, the
Government Accountability Office published an article, clear the
following departments and federal agencies have an important role in
network security: the executive branch, the Department of Homeland
Security, Department of Defense, the Ministry of Commerce, Ministry of
Justice, Department of State. This article will focus on the roles and
responsibilities of these six federal agencies, as they are the main
developer of network security policies and procedures and implementers.
In the executive branch, the newly established "Network security
coordinator" is the primary participants. "Network security coordinator"
is one of the National Security Council and National Economic
Committee, is responsible for ensuring federal network policy can
enhance national security and ensure that the entire government means a
coherent. "Network security coordinator" is a U.S. network security
"pseudo Godfather", although he was responsible directly to the
President, but the lack of funds, and the impact of command of the
people and processes in the field of control over the entire network.
Federal executive branch departments is another influential OMB (Office
of Management and Budget) and its affiliated e-government and
information technology office (Office of E-Government and Information
Technology, E-Gov). E-government and information technology by the
Federal Office of the Chief Information Officer (CIO) is responsible, is
responsible for the development and use of "Internet-based technologies
enable citizens and businesses to interact with the federal government
to become more efficient, saving taxpayers' money, and simplify citizens
participate. "• Mr. Steven 瓦洛伊克尔 America's second federal CIO, on
August 5, 2011 appointed by President Barack Obama. He replaces Mr.
Wei-dimensional Delaunay • hole cards, cards • hole Drouin Victoria Wei
is the first U.S. federal chief information officer shall hold office
from March 2009 to August 2011, also appointed by President Obama.
Federal Chief Information Officer, Chief Information Officer is
responsible for the management committee (CIO Council), Chief
Information Officer Council is "to improve federal information resources
planning, procurement, development, modernization, use, sharing, and
practices related to the implementation of major inter-agency
organization committee" The committee consists of 28 members from
various federal agencies and several other specific federal agencies is /
one of the many dedicated Board Committee is responsible for managing
network security administrations established. Another important
committee in the federal government information and high-level
inter-agency communication infrastructure policy committee (Information
and Communications Infrastructure Interagency Policy Committee,
ICI-IPC), the National Security Council and the Homeland Security
Committee (Homeland Security Council, HSC) is responsible. Information
and communication infrastructure between the Policy Committee is to
coordinate the main body of information and communication infrastructure
policy.
According to "Homeland Security Presidential Decree No. 23" and
"National Security Presidential Decree No. 54," U.S. Department of
Homeland Security (DHS) official leadership of federal agencies'
protective federal government networks and systems ('dot-gov' domain),
and coordination with the private sector to jointly protect the nation's
critical infrastructure and key resources. "U.S. Department of Homeland
Security Federal Protective primarily responsible for information
technology (IT) infrastructure and data networks. Most network security
functions of the department's focus on national protection and Planning
Department (National Protection & Programs Directorate, NPPD), the
Division continued by the Deputy Minister of the Department of Homeland
Security as a supervisor. National Cyber Security Department (National
Cyber Security Division, NCSD) is one of the Council under the
Department of Homeland Security, is responsible for "the public, private
and international entities collaborate to jointly protect cyberspace
and network U.S. interests." National Cyber Security Office Director
responsible for overseeing the National Cybersecurity and Communications
Integration Center (National Cybersecurity and Communications
Integration Center, NCCIC) and the U.S. Computer Emergency Preparedness
Team (United States Computer Emergency Readiness Team, US-CERT).
National Cybersecurity and Communications Integration Center is an
all-weather operations center, "is responsible for federal, state and
local governments, intelligence and law enforcement community and the
private sector to generate a network and communications running
situation map." U.S. Computer Emergency Response Team is also preparing
an all-weather operations center, the business sector at the national
cybersecurity. It is accountable to the federal civil administration
department (Federal Civil Executive Branch) to provide response support
and network attack protection, and with state and local governments,
industry and international partners on information sharing and
collaboration. U.S. Department of Homeland Security / National Cyber
Security Department is responsible for some of the network
infrastructure from attack protection plans such as the National Network
Emergency Response Coordination Group (National Cyber Response
Coordination Group). The group consists of 13 representatives of federal
agencies, when a nationwide network of serious incidents, the group
responsible for coordinating a federal response synchronized. Another
network security bears an important responsibility within the Department
of Homeland Security Council is the United States Secret Service (US
Secret Service, USSS). October 26, 2001, President Bush signed the "USA
Patriot Act" (Uniting and Strengthening America by Providing Appropriate
Tools Required to Intercept and Obstruct Terrorism, abbreviated as USA
PATRIOT) of the Act directed the U.S. Secret Service to establish a
national electronic crime Special Task Force (Electronic Crimes Task
Forces, ECTFs) network. Electronic crime contingents network not only
brings together federal, state and local law enforcement agencies, but
also prosecutors, private industry and academia. The contingent is one
of the United States responsible for investigating cybercrime many
institutions. U.S. Secret Service's mission is to protect the country's
financial infrastructure and payment systems to ensure the absolute
safety of the U.S. economy, by reducing the "e-crime, financial crime,
computer crime, destruction of the payment system, identity theft and
other types of financial crime arising from financial The total loss. "
Finally, within the Department of Homeland Security, an important
network of institutions need to recognize the Information Sharing and
Analysis Center (Information Sharing and Analysis Center, ISAC). The
agency is to create a partnership between the Department of Homeland
Security and the federal government outside the organization. In 2003,
the U.S. President signed the "Homeland Security Presidential Decree No.
7:" Identifying critical infrastructure, priority, and protection
"(HSPD-7)", states: "The federal government requires that each
department within critical infrastructure sectors establish specific
information-sharing organization, and threat and vulnerability
information to other departments in respect of departments to share. "In
response, many departments have set up an information sharing and
analysis center to meet the" Homeland Security Presidential Decree No. 7
"requirement. At present, has set up 16 Information Sharing and
Analysis Center team, they convened a meeting every quarter: the power
industry, financial services, information technology, ground
transportation, public transportation, telecommunications, water supply,
multi-state cooperation, real estate, research and education, commodity
supply, nuclear, marine, highway, national health, emergency management
and response. All partners have signed a written agreement when
participating in joint exercises networks, as well as to respond to the
crisis in the real world of network events, allowing network operators
around the clock non-federal members of the daily affairs of the problem
and the National Cyber Security and Communications Integration Center
within it agency cooperation. Collaboration with the United States has
become an important means of synchronization and information network
infrastructure to protect federal and non-federal network experts.
Department of Defense (DOD) is mainly responsible for the offensive
and defensive network warfare, and the U.S. Department of Homeland
Security is responsible for the defense of the network operations, in
close cooperation between the two institutions in order to ensure the
full spectrum of combat operations (defense, sniffing and attack) are
very well implemented and synchronized to ensure the country against
cyber threats. A formal Memorandum of Agreement signed in September 2010
by the U.S. Department of Homeland Security and Department of Defense
leaders to strengthen cross-sectoral collaboration and enhance
cooperation, as well as to better define the roles and responsibilities
in order to avoid duplication of work. U.S. Department of Defense has
established a new headquarters in 2010 - U.S. Cyber Command
(USCYBERCOM), which is part of the U.S. Strategic Command's Joint
Command of a second. U.S. Cyber Command's mission is responsible for
the planning, coordination, integration, synchronization and guide the
operation of the Department of Defense information networks and
protective actions, the full spectrum of military leadership cyberspace
operations to ensure U.S. and allied freedom of action in cyberspace,
while weakening the U.S. enemy freedom of action in cyberspace.
U.S. combat forces under the command of network management on
behalf of the various branches of power in the network area: Army Cyber
Command (ARCYBER), Navy Tenth Fleet Cyber Command (FLTCYBERCOM),
Twenty-Fourth Air Force (AFCYBER) and the Navy land Team Cyber Command
(MARFORCYBER). In addition to the composition of the armed services
have operational control over, the U.S. Cyber Command, also has a dual
role the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) and the Central Security
Department Secretary (CSS) Director. U.S. National Security Agency /
Central Security Agency in the field of signals intelligence and
information security password dominate American academia. This is a
national network of military intelligence cooperation and to increase
the power of network management partnerships and collaborative
mechanisms. Three lines of business within the United States Cyber
Command is: U.S. Department of Defense Global Information Grid runs
(IT network management); defensive cyberspace operations (to prevent
network attacks) and offensive cyberspace operations (network sniffer
and network attacks) . Similarly, the Department of Defense network
sniffer and network attacks primary leadership duties.
U.S. Department of Commerce (Department of Commerce, DOC) is
another important bodies within the national network security framework,
is primarily responsible for technical improvements to the network
system and the establishment of critical IT infrastructure plan template
for the federal network. Network command of the U.S. Department of
Commerce's 1950 "Defense Production Act," given the aim of reducing the
supply and consumption of federal agencies to meet defense needs. In
computer network security, the U.S. Commerce Department has two
important institutions, the National Institute of Standards and
Technology (National Institute of Standards and Technology, NIST) and
the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (National
Telecommunications and Information Administration, NTIA). National
Institute of Standards and Technology is the U.S. Department of Commerce
to carry out research, development, technology and engineering (RDT
& E) power. Based primarily on safety standards, indicators and best
practices, is responsible for the commercial and government entities to
develop, test, advocacy, monitoring and measurement of new information
technology (IT) principles and technical details. National
Telecommunications and Information Administration is to provide direct
support to the executive branch agencies, is responsible for making
recommendations to the President on telecommunications and information
policy issues. National Telecommunications and Information
Administration's planning and decision-making is largely concentrated in
the United States to expand access to and use of broadband Internet.
National Telecommunications and Information Administration to develop
policies related to the Internet economy, including online privacy,
global free flow of network security, online information.
U.S. Department of Justice (Department of Justice, DOJ) is the
chief law enforcement agency of the U.S. government, is responsible for
the development of network participation and legal rules established by
the U.S. Congress, and those who violate the laws of network-related
individuals, businesses, institutions, state and national institute
litigation. A subordinate agency of the U.S. Department of Justice FBI
(Federal Bureau of Investigations, FBI), is primarily responsible for
the investigation and prosecution of cybercrime problem nationwide
business. The FBI's cybersecurity mission is to investigate high-tech
crimes, such as network-based terrorism, computer intrusions, online
pornography crime and major online fraud. The FBI is responsible from
the public and private sectors, commercial enterprises and other federal
agencies to gather information to analyze forensic evidence cybercrime
incident to determine the source or originator of malicious activity.
The FBI and other law enforcement agencies (federal, state, local and
international agencies) work together to protect and defend the country
against the threat of terrorists and foreign sectors, so as to maintain
and consolidate the American criminal law. National Network survey
jointly contingent (National Cyber Investigative Joint Task Force,
NCIJTF) by the FBI in charge of management, including representatives
from the U.S. Secret Service and other federal agencies. Web survey
organizations as inter-agency coordination of national authorities
responsible for the coordination, integration and sharing of relevant
information about the investigation of cyber threats.
The State (Department of State, DOS) is the lead agency responsible
for foreign affairs and, therefore, has an important role in the
formulation, coordination and supervision of international
communications and information policy implementation. According to the
2003 "Protection of national cyberspace security strategy," the State
Council was given the strengthening of international cooperation in
cyberspace security federal leadership responsibilities. In order to
better fulfill their leadership responsibilities departments, many
Council was given a specific task. For example, economic, energy and
business affairs bureau / International Communications and Information
Policy Bureau (EEB / CIP) for international telecommunications and
information policy. In addition, the Division of Intelligence and
Research (INR), network Affairs Office provides information on network
security analysis and coordination of international projects to expand
services.
Among federal agencies with roles and responsibilities of network
security continues to improve, obviously network defense operations,
policy development, enforcement, research and development mechanism
exists redundant and repetitive work will continue to exist between the
multiple agencies within the U.S. government . A key reason for this
duality is the network of institutions do not specify an independent
authority with overall responsibility for network security management.
Leaders need unity of command and unity of the regulatory work in what
areas and what financial and human resources need to monitor demand
within a regulatory body? With the resignation of officials in the past
few years, advanced networking, network security management signs of
confusion within the field gradually. These leaders are due to the
Federal High disorganization and mismanagement forced to leave, and
ultimately hinder the process of networking management.
Assessment Network Security Management
With the growing size and power of cyberspace every day, and the
ensuing cyber threats and vulnerabilities have increased exponentially.
Due to the growing cyber threats to national interests and
infrastructure safety hazards, the United States must have a responsive
and efficient, able to solve network security management issues of
global cyberspace, time has become an important factor in ensuring this
capability. "The U.S. government is facing a series of tough challenges
that hindered its responsibilities to develop and implement a structured
program" on global cyberspace, includes: (1) to provide the highest
authority of the leadership relationship; (2) develop a coherent and
comprehensive strategy; (3) cross-sectoral coordination among all
relevant federal entities; (4) ensure that the network of space-related
technical standards and policies do not create unnecessary obstacles to
U.S. trade; (5) participation in international network incident
response; (6) distinguish between different legal systems and the
implementation of the U.S. criminal and civil law; international
standards (7) regulate cyberspace. To meet these challenges it is widely
recognized, special assistant to the president and "network security
coordinator" must collaborate with other federal agencies and the
private sector work together to build a united front to the development
of network capacity to meet our country's economic and national security
interests.
In 2010 the U.S. Government Accountability Office review of
national cybersecurity policies and procedures during the period, the
federal government and no clear organizational structure can effectively
resolve the current or future increasingly serious network security
problems. Network security management tasks and responsibilities to be
distributed to a number of federal departments and agencies, there are
many overlapping agencies, but which organizations are no absolute
decision-making power, in a coordinated manner can deal with those
problems are often conflicting directly. Governments need to integrate
strategic vision and plan must be comprehensive, so as to meet the U.S.
government to solve network security-related issues facing the demand.
The United States needs to mitigate network security risks associated
with the development of policies, procedures, personnel and technology.
• Max Stier, said: "The U.S. government has long been the leader in
the use of leverage resources and relationships to form and train a
skilled web team", this team should be reasonable network structure,
carefully consider the interests of citizens and the state, totally
focused At block network threats and vulnerabilities. In the "network
security" troika ": government, private sector partners and citizens
involved in network security," the article, the authors Huck nits and
Stever said: "The security of the network and on the full participation
of knowledgeable citizens The demand must be reasonable and proper
management of the government's structural demand for par. "They stressed
the importance between the U.S. government and citizens to maintain an
appropriate balance of responsibilities, because if every citizen is not
a participant in the network security, national security Cyberspace
goal will never be achieved. To succeed, the government must establish a
personal relationship with IT partners to protect the people, not just
the beneficiaries of the security policy. Unresolved question is, "Which
federal agency responsible?"
By the 2011 "National Security Strategy Cyberspace" can be seen,
the U.S. government has recognized the protection of cyberspace has
become a global problem, because interconnected global computer systems,
is necessary to adopt a global approach to protect information and
prevent infrastructure and economic threats. To reduce network threats,
concerted international cooperation and coordination mechanisms need for
more open communication and trust. In the past few years, network
engineers, incident response, policy makers, intelligence analysts and
law enforcement personnel in this field has made tremendous progress,
and recognizing the transnational sharing of information and network
security solutions into the global transnational security issues
importance. Greater obstacle is the security and integrity of data and
to facilitate information gathering and sharing process. Within the
current U.S. government multi-agency network structure and network
repetitive work, American citizens and business owners decide to which
federal agencies to seek support and assistance will be a daunting task,
but the more difficult task is how the international community to fully
realize the American network support. Despite the official
pre-coordinated agreements, policies and information sharing treaty
reduces the time interval, but new threats into the World Network of
tactics, techniques and procedures often require new solutions and
respond to new partners; This makes the agreement has been approved
outdated or obsolete.
As we all know, yesterday, skilled hackers "zero day
vulnerabilities" to block or disrupt networks, affirmation and
tomorrow's advanced persistent threats (advanced persistent threat, APT)
can not match, advanced persistent threats to national and non-national
criminal organizations stealing intellectual property rights and to
engage in criminal activity means new threats. The international
community needs a safe and secure network, in this network, critical
information can be freely across network boundaries, by reliance on the
protection of the infrastructure has been promoted to a global interest,
not only national interests. To always be on the growing threat of a
global network to stay ahead, America's international partners should
have a centralized organization, and "one-stop" agency to collaborative
network security issues. Unresolved question is, "Which federal
institutions are responsible?"
Protection of the global cyberspace needs of individuals, public,
private, local, state, federal, and international cooperation to jointly
improve situational awareness, share information, and promote safety
standards, and cyber crime investigations and litigation. In order to
achieve the objectives of the proper management of network security, not
only for America, but for the entire world, it is very necessary to set
up a joint body in the United States, which will improve network
security overall stability and security.
Strategic plan to improve network security management
Review roles and responsibilities of each federal agency, and to
assess the network security management, the author of the U.S. to solve
global problems and improve cyberspace network management currently
three options put forward suggestions: (1) maintain the existing
organizational structure; ( 2) re-adjust the organizational structure;
(3) the formation of a new network of institutions. Let the benefits of
each program, shortcomings and to focus on the strategic impact
analysis.
Option One (keeping the existing organizational structure). This
program requires no change in the current organizational structure of
the national security agencies and federal agencies. As the Special
Assistant to the President and the "Network security coordinator" in
December 2009, appointed a new job, but the network of institutions in
its network security management activities is still in its infancy, has
not yet developed into a management elements have absolute authority.
Through the accumulation of time and experience to keep the existing
structure of this program will improve the overall management of the
network area. The biggest advantage of this program is no cost burden.
Over time, the "shrinking" of the financial needs and improve the
coordinator positions can satisfy the current need to cut government
spending in the economy, because this program is no restructuring of the
financial burden. The disadvantage of this program are: the shortage of
heavy workload required; tasks and roles and responsibilities defined
priority unresolved; network security operations and policy makers have
not yet timely manner. Potential strategic impact has three aspects: (1)
Due to policy development and information exchange is not synchronized,
which increases the number of attacks and network latency network
incident response efficiency; (2) Due to limited regulatory oversight,
coordination of the international community of network will be reduced;
(3) increase the recovery of infrastructure being attacked restoration
costs. All of these issues are on the national security interests of
diplomacy and economic measures pose a serious risk.
Option II (re-adjust the organizational structure). This program
proposes to set up a government department level "network committee", by
members of the representatives of various federal institutional
stakeholders composition, and their command and control delegated to the
"Network Security Coordinator office." This program is envisioned the
establishment of a new special team comprising more than 20 members, the
organization can establish a direct mechanism for sharing "Network
security coordinator" of the heavy workload. Establish a constructive
and skilled staff agencies, government departments and federal agencies
will be of great benefit, because timely and effective inter-agency
communication will henceforth become a reality. With this program would
require federal agencies involved in the development of new
organizational structures. Other advantages include: a balanced
allocation of priority allocation, division of responsibilities,
workload and enhance cross-border collaboration. Global information
exchange by members of the "Network committee" to participate in policy
and procedures, as well as attacks on the network response actions,
international advantage can be achieved. The disadvantage is high than
maintaining the existing organizational structure of the program's
costs. But because the office space allocation and personnel
resettlement cost will be reduced to a minimum. Compared with Option One
and Option III, taking the strategic impact of such programs will be
significantly reduced. All national power (diplomatic, intelligence,
military, and economic) to achieve successful integration, by
strengthening global partnerships; optimize the management and
organizational structure; dissuade and deter cyber threats and prevent
further recession. Periodically readjust personnel from other federal
agencies is absolutely feasible. Although the relationship between
leadership and coordination to improve the effect is significant, but
this solution does not solve the problem of the lack of budget for
network security management rights.
Option III (the formation of a new network of institutions). Such
programs need to create a new federal agency, is responsible for leading
all network related activities, including the development and
implementation of policies and procedures; synchronize information
sharing and coordination among network service local, state, federal and
international equivalent bodies; monitoring network in the field
intrusion; organization cybercrime forensic analysis; coordination of
intelligence and law enforcement; perform research, development,
technology and engineering and the development of a comprehensive
strategy. Network Coordinator will continue as an important member of
the President's Office, to report on the latest developments of national
networks and government members to the President, the White House and
become the liaison between the new Cyber Command.
Reduce duplication of efforts and resources management efforts
currently under intense process, organizations should conduct a detailed
assessment of all federal agencies to determine the potential
restructuring of the network elements. This is an external agency of the
federal government needs to lead the assessment team, composed of
representatives of the assessment team members federal departments and
agencies. The formation of a new headquarters members or from other
existing federal sector jobs, and hire new employees or adjusted. After a
program using new and existing federal employees to establish a joint
body, this program is to prevent damage to the overall historic
institutions and creating new jobs in the preferred solution. Members of
these possible merger policy makers, research and development
scientists, federal network operations centers and intelligence
analysts. The creation of a new agency will not weaken the demand for
inter-agency communication and collaboration; Indeed, the need for
communication and collaboration in this inter-agency will be greater.
The current government is a net environmental systems and electricity
networks, and long-term existence. Intelligence, economic, military, law
enforcement and foreign affairs management, not only by a separate
federal agency management, and each factor is also a subset of the
various federal agencies. For example, each department currently has an
international security cooperation qualifications, a budget department, a
legal and policy sectors and a network of threat analysis organization,
it can be said network management and communications and information
management basically similar. Although the network is among the common
elements of all federal agencies, the future network services in the
public, private and federal sector will continue to grow exponentially.
The world's only just in the early stages of information technology,
including network attacks and network security. If the majority of the
American networks are located in the private sector, the majority of
network security risks also exist in this environment, it is mainly
economic issues. The rest of the U.S. networks, such as: ". Gov" and ".
Mil" network, charged with the important task of protecting sensitive or
confidential information, and these networks have been well protected.
The disadvantage of this approach is the need to give consideration to
create a new institution.
Proposal
Due to current molecular criminals and terrorists continue to
infiltrate the Global Information Grid, protect U.S. security interests
core becomes critical. However, in order to achieve significant progress
in cyberspace management, time becomes an important factor in ensuring
this capability. In the short term in order to ensure both get immediate
results, but also minimize the use of resources, the best option is
Option Two: Re-adjust the current organizational structure. This program
meets strong leadership; improve global collaboration and inter-agency;
timely develop and implement policies and procedures; improve oversight
of network operations; enhanced situational awareness as well as
national security reduce economic costs. The key to success is a
rational structure of regulatory agencies, for directing, guiding and
promoting the network security team has absolute power. Option Two is to
solve the current shortage of network security management framework the
best choice.
However, long-term solution is still the plan three, create a new
network of institutions. Build a new headquarters in the United States
not only improve network management capabilities, but also that the
United States has to the international community as a national
cybersecurity priority development projects, and can create a real sense
of the enemy other nation-states and non-nation-state's network edge.
Other advantages of this approach is that the command of centralized
decision-making focus, reduce repetitive work and clear distinction
between the tasks and responsibilities. Although you can propose a
feasible demand a declaration that based on the current threat is
absolutely necessary to set up a new network security federal agencies,
the time and resources required to obtain congressional approval, and
the establishment of an effective and efficient organization, which is
undoubtedly a complex arduous and difficult task. Also need to respond
to the current financial burden of reduced economic spending plan, and
may lead to unrest within the public sector; Although you can create new
jobs. A comprehensive strategic roadmap and strong strategic
communications plan will need approval from Congress and the general
public to actively support for this program.
Conclusion
Our country's top decision-makers must consider the adoption of
long-term strategic plan to ensure that the United States can rely on
the safe use of cyberspace. So far, the U.S. government has taken
measures to deal with the traditional network security issues - these
measures failed to achieve the desired results. 2008 "Comprehensive
National Cybersecurity Plan" and the subsequent series of efforts aimed
at the establishment of a network defense strategy to make some attempt,
by improving early warning capability to deter cyberspace interference
and attacks; clear the private sector and international partners task;
and develop a reasonable response to the State and non-State actors.
New, non-traditional network security measures need to completely
break the current network security organization inefficient "rice bowl"
of protectionism. Intelligence sharing government and the private sector
between network security operations center will be the first and most
important step. Federal cybersecurity organizations and the ability to
integrate (to reduce duplication of work and business to a minimum), it
may be cost savings and enhance our national cybersecurity posture of
the second step. Increasingly savvy leader has absolute power in
cyberspace is the third step. Huge capital expenditures how we will
solve the problem and deal with national cybersecurity coordinated
action to change this culture is enormous challenges we currently face.